Products
Iodixanol Injection, USP
Fresenius Kabi’s FDA-approved generic Iodixanol is made with quality ingredients and is safe and effective. Iodixanol provides you with an option that is bioequivalent and fully substitutable to Visipaque®.* Now you have a choice.
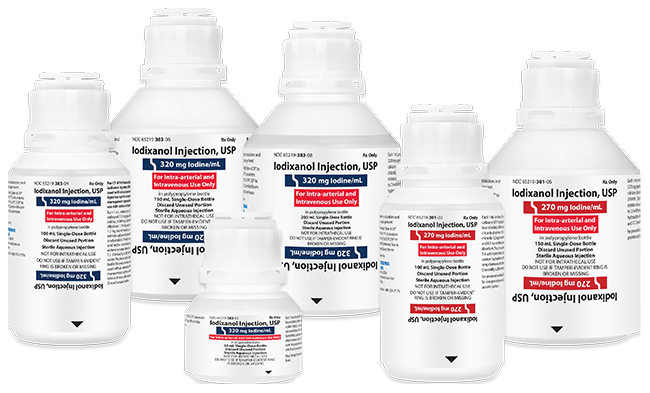
Iso-Osmolar, Dimeric Iodinated
Contrast Agent2
Fresenius Kabi’s Iodixanol Injection, USP is fully substitutable to Visipaque®.*
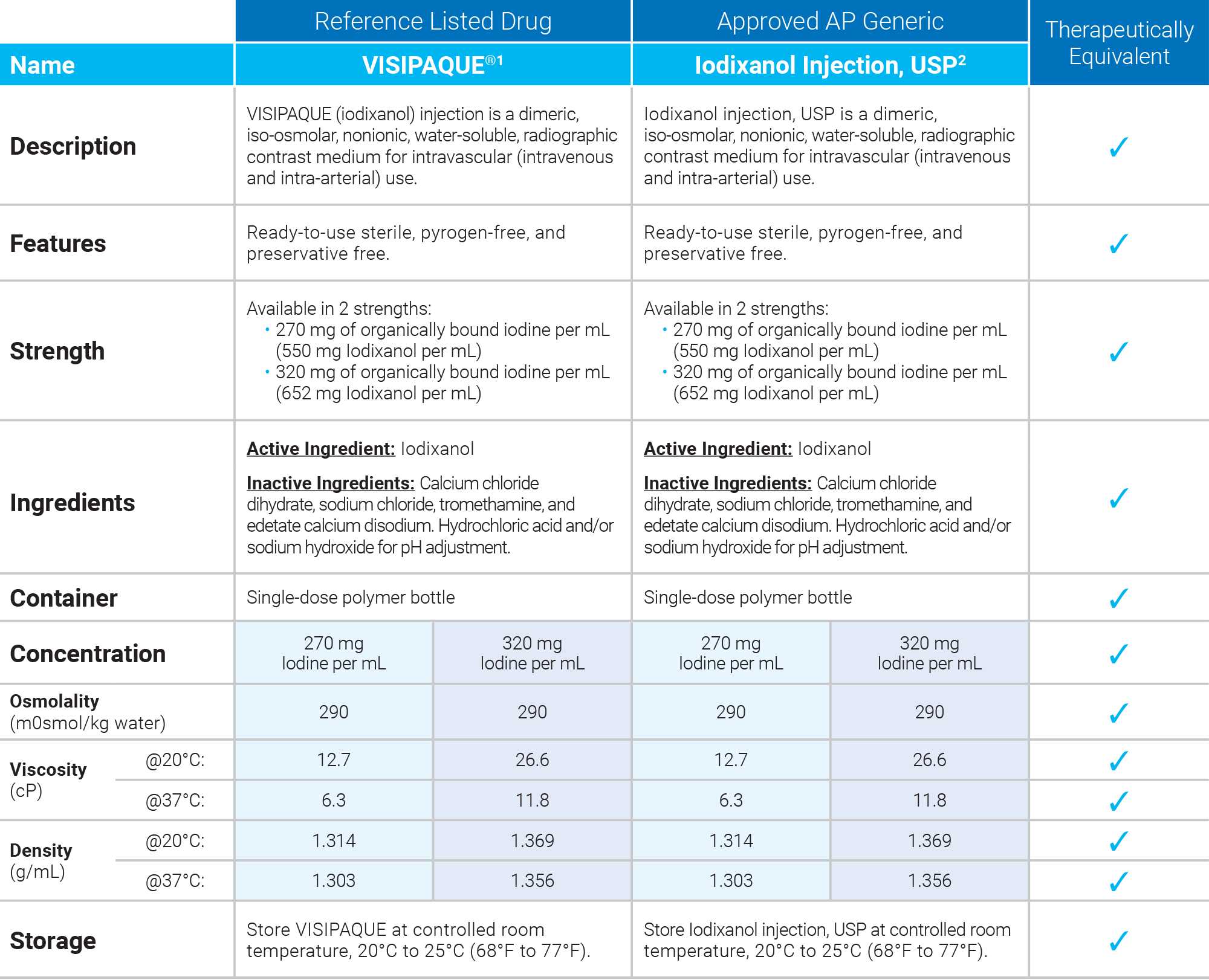
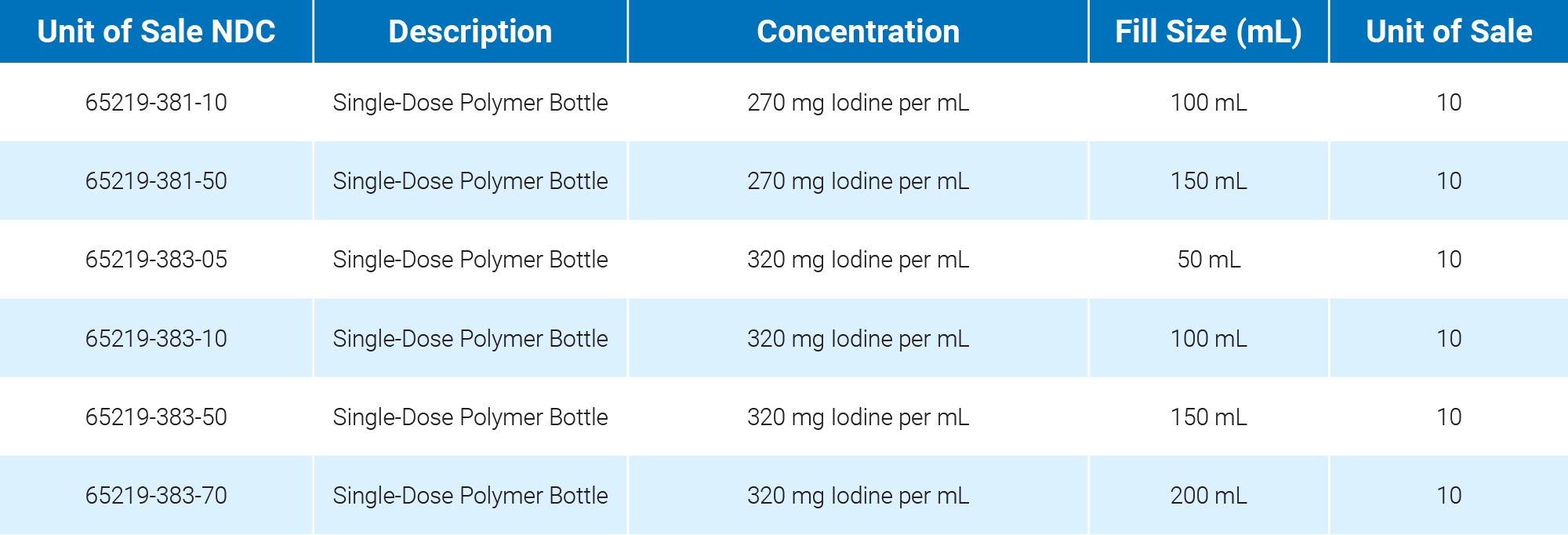
1. Visipaque Package Insert, July 2020
2. Iodixanol Injection, USP Package Insert, May 2023
Iodixanol Injection, USP
• Iso-Osmolar2
• Dimeric2
• FDA-approved, AP Rated
• Preservative Free2
• Polymer Bottle
• Container is not made with natural rubber latex
• Fully substitutable and bioequivalent to Visipaque®*
Important Safety Information
WARNING: NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE
Inadvertent intrathecal administration may cause death, convulsions/seizures, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema.
Contraindications: Iodixanol Injection is contraindicated for intrathecal use.
Warnings and Precautions:
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Life-threatening or fatal reactions can occur. Most severe reactions develop shortly after the start of the injection, but reactions can occur up to hours later. Always have emergency equipment and trained personnel available.
Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Acute injury including renal failure can occur. Minimize dose and maintain adequate hydration to minimize risk.
Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions: Life-threatening or fatal cardiovascular reactions, including hypotension, shock, and cardiac arrest have occurred with the use of Iodixanol. Most deaths occur during injection or five to ten minutes later, with cardiovascular disease as the main aggravating factor. Use the lowest necessary dose of Iodixanol in patients with congestive heart failure.
Thromboembolic Events: Serious, rarely fatal, thromboembolic events causing myocardial infarction and stroke can occur during angiocardiography procedures with both ionic and nonionic contrast agents.
Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Extravasation of Iodixanol injection may cause tissue necrosis and/or compartment syndrome, particularly in patients with severe arterial or venous disease. Ensure intravascular placement of catheters prior to injection.
Thyroid Storm in Patients with Hyperthyroidism: Thyroid storm has occurred after the intravascular use of iodinated contrast agents in patients with hyperthyroidism, or with an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule.
Thyroid Dysfunction in Pediatric Patients 0 to 3 Years of Age: Thyroid dysfunction characterized by hypothyroidism or transient thyroid suppression has been reported after both single exposure and multiple exposures to iodinated contrast media in patients 0 to 3 years of age. After exposure to iodinated contrast media, individualize thyroid function monitoring based on underlying risk factors, especially in term and preterm neonates.
Hypertensive Crisis in Patients with Pheochromocytoma: Hypertensive crisis has occurred after the use of iodinated contrast agents in patients with pheochromocytoma. Inject the minimum amount of contrast necessary, assess the blood pressure throughout the procedure, and have measures for treatment of a hypertensive crisis readily available.
Sickle Cell Crisis in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease: Iodinated contrast agents when administered intravascularly may promote sickling in individuals who are homozygous for sickle cell disease.
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions: Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) may develop from one hour to several weeks after intravascular contrast agent administration. These reactions include Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). Avoid administering iodixanol to patients with a history of a severe cutaneous adverse reaction to iodixanol.
Adverse Events: Serious, life-threatening, and fatal reactions, mostly of cardiovascular origin, have been associated with the administration of iodine-containing contrast agents, including Iodixanol Injection. Most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than 0.5%) in adult patients after iodixanol injection: Discomfort, warmth, pain; Cardiovas¬cular: angina. Gastrointestinal: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Nervous System: agitation, anxiety, insomnia, nervousness, dizziness, headache, migraine, unusual skin sensations, sensory disturbance, fainting, sensation of spinning. Skin: itchy rash, severe itching, hives. Special Senses: Smell, taste, and vision alteration. Pediatric patients experienced similar adverse reactions.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC at 1-800-551-7176, option 5, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Lactation: A lactating woman may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breast milk for 10 hours after iodixanol administration in order to minimize drug exposure to a breast fed infant.
Pediatric Use: Pediatric patients at high risk of adverse reactions during and after administration of contrast agents include those with asthma, hypersensitivity to other medication and/or allergens, cyanotic and acyanotic heart disease, chronic heart failure, or a serum creatinine >1.5 mg/dL. Patients with immature renal function or dehydration may be at increased risk due to prolonged elimination of iodinated contrast agents.
Geriatric Use: Dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Iodixanol injection is a radiographic contrast agent indicated for the following:
Intra-arterial Procedures
Adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and over- Intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (270 mg Iodine/mL and 320 mg Iodine/mL).
- Angiocardiography (left ventriculography and selective coronary arteriography), peripheral arteriography, visceral arteriography, and cerebral arteriography (320 mg Iodine/mL).
- Angiocardiography, cerebral arteriography, and visceral arteriography (320 mg Iodine/mL).
Intravenous Procedures
Adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and over
- Computed tomography (CT) imaging head and body (270 mg Iodine/mL and 320 mg Iodine/mL).
- Excretory urography (270 mg Iodine/mL and 320 mg Iodine/mL).
- Peripheral venography (270 mg Iodine/mL).
- Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) to assist diagnostic evaluation of patients with suspected coronary artery disease (320 mg Iodine/mL).
- CT imaging of the head and body (270 mg Iodine/mL).
- Excretory urography (270 mg Iodine/mL).
This Important Safety Information does not include all the information needed to use Iodixanol Injection, USP safely and effectively. Please see full prescribing information, including BOXED WARNING, for Iodixanol Injection, USP at www.fresenius-kabi.com/us.